OATSystems Professional Services Methodology
OAT's proven implementation methodology delivers RFID solutions
in four key project phases: Scope and Plan, Design and Configure,
Integrate and Test, and Deploy.
1. Scope and Plan
OAT Professional Services consultants formally initiate the implementation
project with a series of discussions with the client to understand
the business environment and requirements from the perspectives
of operations, information technology, and the client's customers
and suppliers. Business requirements are analyzed and mapped
to OAT's software solutions. Key performance indicators (KPI)
are defined to measure project success, improvement goals of
client customer/supplier KPIs, and the expected value from deploying
RFID within the client's logistics operations.
A detailed project plan and resource plan is tailored to the client's
business requirements and presented to the client for review and
approval. A project team is formally identified and gathered for
a project kickoff meeting where the key milestones, deliverables,
and project governance are presented.
2. Design and Configure
An OAT solution architect works with client personnel to develop
detailed use cases that document the business process, production/logistics
environment, product flow, integration messages, exception handling
and user notification. Use cases are reviewed and approved by
the client before implementation work begins. The OAT solution
architect develops test scripts and criteria to test the system
configuration with the client project team.
Information technology personnel are engaged to determine server,
storage, and network requirements. OAT consultants assist the client
in developing a hardware plan and network topology to support the
RFID process.
Operations and facility personnel are engaged to plan the location
of RFID hardware (e.g. readers and antennas). Solution architects
plan appropriate integration with process line controls for seamless
integration into the client's logistics process.
OAT systems engineers establish a development environment and
configure the OAT Foundation Suite based on the approved use cases.
Systems engineers under the direction of the solution architect
conduct unit testing to ensure the system is performing as expected.
Results of the unit tests are presented and reviewed with the client
project team.
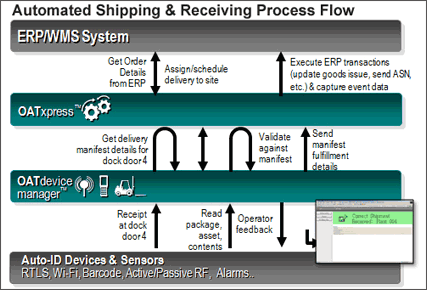
3. Integrate and Test
Achieving the appropriate level of integration between the RFID
process and client ERP, WMS, and planning systems is an important
aspect of a successful an OAT RFID implementation. Integration
requirements are defined within the set of use cases. During
this phase, client infrastructure is established to transport
integration messages and data between systems. OAT systems engineers
create test integration messages that are sent to client systems,
and receive test messages that impact the RFID environment from
these systems. End-to-end test scripts are executed, with the
results documented and reviewed by the project team.
4. Deploy
The tested system is deployed at the client site. The OAT team
works with the client to install software, RFID hardware, and
appropriate process triggers. Complete end-to-end testing of
the systems is conducted on the system with client project team
members. Users are trained on the system, how to interpret user
notifications, and exception handling.
The implementation project is closed with client approval of deliverables
completed.
Project Management and Governance
The OAT project manager will provide overall project leadership and will manage a cross-functional team consisted of OAT and client business, operational, and information technology resources.
Overall responsibilities include development and maintenance of overall project and resource plan, ongoing issues log, weekly status reports, project plan updates and facilitation of key project-related meetings.







 OAT Foundation Suite
OAT Foundation Suite